|
|
|
A, B,
C, D, E,
F, G, H,
I, J, K,
L, M, N,
O, P, Q,
R, S, T,
U, V, W,
X, Y, Z
A
- Absolute Value
-
Not an agreement reached by buyer and seller...
The absolute value of a number is -1 times the number if it
is negative or +1 times the number if it is positive. The absolute value
makes all numbers positive regardless of sign.
Alphabet Links
-
Acceleration
-
An ancestor, twice removed, of displacement...
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity with
respect to time. Acceleration is a vector
quantity. Acceleration is related to the
force on an object and its mass by
Newton's second law, stating that acceleration equals force
divided by mass. A=F/m. The rate of
change of acceleration is called
jerk.
Jerk is equal to the rate of change of the force on an object.
See the notes on acceleration
for more information.
Alphabet Links
-
Active State Change
-
Contrary to Mother Nature's wishes...
Changes in the state of a object that causes the object to depart from the path dictated by inertia. Active state changes involve action by a player outside the object whose state we are tracking.
Alphabet Links
-
Age
-
A tricky subject, fraught with uncertainty...
Age is the current
temporal
extent
of an object. The age of an object could be read from a clock that had
accompanied that object on its path through spacetime, its
world line.
See the age notes for more.
Alphabet Links
- Angular Frequency
-
Time, stood on its head...
The frequency of a periodic system, multiplied by 2π
The units are in radians per unit time
but since radians are unitless, it comes
out to be t-1, the same as angular velocity of circular motion.
Angular frequency is symbolized by the Greek letter omega ω.
Alphabet Links
-
Angular Momentum
-
Angular momentum is the product of a vector quantity, angular velocity, and a
scalar quantity, moment of inertia.
Alphabet Links
-
Angular Velocity
-
Entry text
Alphabet Links
- Applied Force
-
As that of the hammer on a nail...
We make a somewhat arbitrary distinction among the
forces acting in a
dynamical system.
The categories are applied force,
centering force
and drag or
friction force.
The applied force is taken to be that force which is applied to the moving parts
of a system by an outside agent as for example the force applied to a pendulum
by someone pushing it or the force applied to a piece of metal by the magnetic
field of an electromagnet. An applied force results in an energy transfer
across the system boundary.
Alphabet Links
- Attractor
-
Where a system is contented...
An attractor is a particular
state or
set of states of a
dynamical system
that the system seeks as time passes. For instance a pendulum with
friction will eventually come to rest hanging straight
down with zero velocity. The point (0,0) then is an attractor for an undriven
pendulum. Attractors may also be
periodic,
consisting of a set of states that the system visits, one after another,
repeatedly. Periodic attractors may be finite or infinite sets. Another
category of attractor is
chaotic.
Chaotic attractors consist of an infinite set of states that never repeat but
are all contained in a finite volume of
phase space.
Alphabet Links
B
-
Basin of Attraction
-
The collection of starting places for things ending together...
If a
dynamical system
eventually settles down to no motion,
periodic motion or
bounded chaotic
motion, it is said to have settled on its
attractor. It is possible that a system have multiple attractors and which long-term
state of motion the systems seeks depends on its initial state. The
set
of all initial states that lead to a certain attractor is called that attractor's basin of attraction.
Alphabet Links
-
Bifurcation
-
The point where one becomes two...
In general a bifurcation is a splitting or branching of an
object.
With regard to an
attractor,
it refers to a doubling of the number of points in a finite
periodic
attractor as a
control variable
changes.
Alphabet Links
-
Big Bang
-
Marking the absolute zero of time...
The Big Bang is the name given to the event that seems to have originated the
universe. I don't think I can do better describing it than to refer you to the
Wikipedia article on it. See
Big Bang Timeline
Alphabet Links
C
-
Causal Relationship
-
The relationship between cause and effect...
Two events have a causal relationship if one caused the other. The caused event
is often called the effect. The
Spacetime
Interval
between cause and effect must be time-like or light-like.
Alphabet Links
- Centering Force
-
The poor thing is hardly ever satisfied...
We make a somewhat arbitrary distinction among the
forces acting in a
dynamical system.
The categories are
applied force
centering, sometimes called restoring, force and drag or
friction force.
The centering force is taken to be that force which tends to restore the system
to some equilibrium state
as for example the force applied to a pendulum by gravity. A centering force
does not result in an energy transfer across the system boundary since the
centering agent is customarily taken to be part of the system.
Alphabet Links
- Chaotic
-
This is highly irregular...
Chaotic is an adjective describing a
dynamical system or mathematical
function
in which future
states
or values are not related in any simple way to the current state or value. It
is not to imply that there is no connection between past and future states or
values, only that the connection is so complex as to make prediction of the
future from the past a practical impossibility. If the
set
of future states or values, though unpredictable, is limited to a finite
range of values, the system or function is said to be
bounded as well as chaotic.
Alphabet Links
-
Comoving Frame
-
A reference frame favored by Nature...
The comoving reference frame is the frame in which the cosmic microwave
background (See the
Wikipedia article on CMB.) appears isotropic, unvarying with respect to
direction. For details I refer you to the Wikipedia article on
Comoving Coordinates.
Alphabet Links
- Complex Number
-
Not so much complex as complete...
Ordinary numbers that we use for accounting and simple calculations are called
real numbers. There is no real number such that the square of that number is -1
since the product of any real number with itself is positive. To remedy this
situation, the square root of -1 was defined and given the symbol i. Then a new
class of numbers was invented, called imaginary numbers, made up of i times the
set of real numbers. A complex number is a number comprised
of a real part added to an imaginary part like a+b*i. See the
notes on complex numbers for more.
Alphabet Links
- Complex Plane
-
Where the imaginary is joined to the real...
The complex plane contains the
set
of complex numbers. It is a plane spanned by the
set of real numbers, normally along the horizontal axis, and the set of
imaginary numbers, normally along the vertical axis. See the
notes on complex numbers for more.
Alphabet Links
-
Component
-
An element of a composition...
Literally components are things from which something else is composed. For
our purposes it usually applies to a vector. Any vector
can be expressed as the sum of a pair of perpendicular vectors. These
perpendicular vectors are called the components of the initial vector. See the
vector arithmetic page for more detail.
Alphabet Links
- Conservative System
-
Having nothing to do with politics...
A dynamical system in which
no energy is either lost or gained by the
system. These are systems where friction is negligible.
Alphabet Links
-
Contemporaries
-
A pair of objects that have an opportunity to interact...
In common usage, contemporaries are objects whose lifetimes overlap. In the
heading above, I propose a modified definition taking into account the effects
of relativity. See the
notes on contemporaries for more.
Alphabet Links
-
Continuum
-
Everywhere dense and smooth...
Continuum – a continuous thing with no gaps or jumps however closely examined.
Alphabet Links
- Control Parameter
-
Sort of like the volume control on your stereo...
In a
dynamical system or mathematical
function,
the defining
equation
may contain parameters that are either constant, or subject to change. Those
that are subject to change are called control parameters. For example in the
equation Y=A*exp(-(b-X)2)
if the parameter A can be adjusted between runs through the
domain of X, A would be a control parameter.
Alphabet Links
- Converge
-
Closing in on something...
If the dependent variable of a function under
iteration
gets closer and closer to a fixed value the function is said to converge under
iteration.
Alphabet Links
-
Conversion Factors
-
e.g Horsepower to stoneweight furlongs/fortnight...
A conversion factor is a number by which we multiply one unit, a meter of length
for example, to get that same length expressed in other units, centimeters for
example. In this case the conversion factor is 100. Multiply 10 meters by 100
centimeters per meter to get 1000 centimeters. The conversion factor may be
decided by tradition, committee work or Nature. See
Converting time to distance for another
example.
Alphabet Links
- Cosine
-
Companion to the sine...
In a right triangle, the cosine is the ratio of the adjacent side to the
hypotenuse. See the trigonometric functions
page for more.
Alphabet Links
- Cycle
-
Everything from goes around to comes around...
The
set of all the states or values visited by a
periodic system or
function
during one
period.
In other words one cycle of anything that is repetitive is everything it does
before repeating.
Alphabet Links
D
- Density
-
Makes small objects heavy...
The mass per unit volume of an object. It would be measured
in kilograms per cubic meter in the SI system
of units.
Alphabet Links
-
Dimension
-
Extent or manifoldness...
The word dimension is commonly used in two ways. The size of a thing is given
by its dimensions as in, "This is how you are to make it: the length of the ark
three hundred cubits, its breadth fifty cubits, and its height thirty cubits."
The other usage identifies the number of dimensions of a space as in, "We live
in a three-dimensional space." It is normally clear from the context which
usage is intended.
Alphabet Links
-
Displacement
-
Start subtracted from finish...
Displacement is the difference between a final
position and an initial one. Displacement is a
vector quantity, not necessarily the path length.
Alphabet Links
-
Distance
-
Not taking time into account...
Distance is the separation in
space
between two
particles
or
events.
Alphabet Links
- Diverge
-
Receding, to be seen no more...
If absolute value
of the dependent variable of a function under
iteration
increases without limit the function is said to diverge under iteration.
Alphabet Links
-
Domain
-
The home of independent variables...
The domain is the
set
of values that the independent variable of a
function
may take on. A domain may be finite as in the set of numbers {1, 2, 3..n} or
infinite as in all the numbers between 0 and 1.
Alphabet Links
-
Dynamical System
-
Different today than yesterday...
A system that changes with the passage of time. Basically
that is any system with moving parts.
Alphabet Links
- Dynamics
-
Not statics...
The study of motion and the forces which
cause it.
Alphabet Links
E
-
Effective Mass
-
A great simplification of reality...
The mass in a dynamical system that must be
included when we treat the moving parts of the system as though
they were a particle , using the free body analysis in applying Newton's laws of motion .
Alphabet Links
- Elastic Scattering
-
Not rubber bands scurrying off in all directions...
An interaction where two particles collide and the total kinetic energy of the two particles
remains constant. The direction and speed of both particles will
in general be different after the collision.
Alphabet Links
- Energy
-
Enables us to get up and do things...
Classically energy is defined as the ability of an object to do work on its surroundings. It may be in the form
of kinetic energy or of potential energy . In relativity
mass is included in energy according to
E=mc2.
See the energy notes for more.
Alphabet Links
- Entropy
-
Hinders us from getting up and doing things...
Entropy may be thought of as a way to quantify the inability to get things done.
The greater the entropy of a system, the less work it can accomplish. A
collection of objects at rest relative to each other, with no forces acting
between them and at the same temperature as their surroundings could not have
much impact on their universe. That would be a high entropy
system. Entropy and
energy
are in a sense inverses of each other. High entropy systems are characterized
by uniformity. If nothing distinguishes one location in space from another,
there is no motivation for objects to change positions or otherwise get involved
in the goings on of their universe. High energy systems are characterized by
distinction. High is different than low, fast is different than slow and hot is
different than cold.
Alphabet Links
- Equation
-
An eternal truth...
An equation is a mathematical expression with an equal sign (=) in it. It
signifies that the numerical or vector value on one side
of the = is the same as the numerical or vector value on the other side. An
equation may include variables and
parameters. If any of the variables are rates of
change, the equation is called a differential equation.
Alphabet Links
- Event
-
A happening thing...
An event is an occurrence that may be considered localized in spacetime,
identified with specific values of the space and time coordinates.
See notes on events for more.
Alphabet Links
-
Exponentiation
-
Shorthand for multiple multiplications...
Raising a number to a power. The expression be means
multiply b (the base) by itself e (the exponent) times.
Alphabet Links
-
Extent
-
The reach of a thing...
The size of a thing in spacetime, spanning a certain
range in each of the three spatial dimensions and a certain duration in time.
Alphabet Links
F
-
Fluid
-
Making a career of shapelessness...
Fluid is material that takes the shape of its container. It may be a gas which
expands to fill the entire volume of its container or liquid which settles into
the bottom of its container. An alternative definition of fluid is that it is
material that does not support shear forces.
Alphabet Links
- Force
-
Causing immediate acceleration...
Quite simply a force is a push or a pull. Force is a vector quantity.
Alphabet Links
- Free Body
-
Having nothing to do with scandalous behavior...
An object that is unconstrained so that
it may respond to forces in accordance with Newton's laws of motion.
Alphabet Links
- Frequency
-
Rapidity of recurrence...
The number of cycles per unit
time that a periodic system or function
completes. The frequency (f) is related to the
period (T) by f=1/T.
Alphabet Links
-
Friction
-
Allowing us to get a grip...
We consider two kinds of friction, sliding friction and turbulent friction.
Sliding friction occurs when two solid objects maintain contact with one another
while in relative motion. The small hills and valleys on the surfaces tend to
get caught on one another as they pass, requiring force
to be applied to keep the motion going. The reaction to this applied force is
called the force of sliding friction. The work
done by the applied force raises the temperature of the objects. The force
perpendicular to the motion, holding the surfaces of the objects together,
is called the normal force. Turbulent friction occurs
when an object moves through a fluid medium, stirring it up
and losing some of its kinetic energy
to the medium. This situation also requires the application of a force to keep
the motion going and the reaction to that force is the force of turbulent
friction. The work done by the applied force raises the temperature of the
object and the surrounding fluid.
Alphabet Links
-
Function
-
Mathematicians have moved on, but for us...
A mathematical function is a rule relating two
sets
of objects. Here we will restrict ourselves to objects that are numbers or
vectors. One of the sets is called the
domain
of the function, the other is called the
range
of the function. Functions are frequently expressed as
equations as for example
Y=X+2.
This function is interpreted as follows. For every X in the domain, add 2 to it
to get the corresponding Y in the range. Because we are free to choose any X we
want, X is called the independent variable. Because once X is chosen Y is fixed,
we call Y the dependent variable.
Alphabet Links
- Future
-
Different from the past and not what we think...
Future – the
continuum
of
time
later than
now.
Alphabet Links
G
- Gaussian
-
Why no one is normal...
The bell shaped curve that is used to describe the
distribution of quantities around some normal value, named in
honor of Mr. Gauss we believe. This
function is expressed as
Y=A*exp(-(b-X)2) , where "A"
is the amplitude or height of the curve and "b" is the
location of the peak of the curve on the X axis. The exp() symbol
represents the number "e" (approximately equal to
2.7182818284), raised to the power of the stuff in its
parentheses. For example exp(0)=1, exp(1)=e, exp(2)=e2,
exp(-1)=1/e, exp(-2)=1/(e2), and so on. As you can see when X=b,
Y=A in the Gaussian function. As X departs from b in either
direction, the value of the exp() approaches zero, forcing Y to
approach zero as well. See the Non-Linear Rate of Change display
in the Rate of Change lesson for an
illustration
Alphabet Links
-
Geodesic
-
Nature's preferred path...
A geodesic is a curve in space that minimizes or maximizes a certain parameter
along its length. In flat 3-dimensional space geodesics are straight lines that
minimize the distance between two points. On the curved 2-dimensional surface
of a globe the geodesics are "great circles", like lines of longitude. A string
stretched tight between two points on a globe, minimizing the distance between
them, will lie along a great circle. In 4-dimensional
spacetime, the geodesics
are curves that maximize aging for an object traveling that path. In flat
spacetime geodesics between events are straight lines
Alphabet Links
-
Gravity
-
With the endless task of keeping it all together...
Gravity is one of the four fundamental forces
of Nature. It acts on all mass over all distances and is a purely attractive force
proportional to the product of the two masses involved divided by the square of
the distance between them. It is, by a factor of about 1040 the
weakest of the fundamental forces. It is so weak that it requires an object the
mass of the Earth to make a pound of butter weigh a pound. See the
notes on gravity for more information.
Alphabet Links
H
-
-
No entry here yet.
Alphabet Links
I
- Impulse Force
-
Having nothing to do with rash behavior...
A force applied for a time which is short compared to the
observation time, as for example the force between a bat and ball
where the observation is over the entire flight of the ball from
leaving the pitcher's hand to landing in the bleachers.
Alphabet Links
-
Inertia
-
A manifestation of the Nature's laziness...
Inertia is the resistance of any physical object to a change in its state of motion or rest. It is proportional to an object's mass. The path an object follows under the influence of inertia is a spacetime curve called a geodesic. In flat spacetime geodesics are straight lines.
Alphabet Links
-
Interval
-
The one thing in spacetime on which one may depend...
Interval – the separation in spacetime
between two events. The spacetime interval between two events is invariant among
reference frames. See the
interval notes for more.
Alphabet Links
-
Instant
-
A short enough span of time that shorter makes no difference...
Instant – an extent
of time so short that in the context its duration may be
neglected.
Alphabet Links
- Iteration
-
Getting infinite variety from simple repetition ...
Iteration is the process of taking the value of the dependent variable of a
function
and feeding it back into the function as the independent variable.
Alphabet Links
J
-
Julia Set
-
Gaston Julia had some sets...
A Julia set, named for Gaston Julia, is the
set of all points in the
complex plane
such that the
iterated
function
Zn=Z(n-1)2+k,
where k is a fixed
complex number,
does not
diverge
as n approaches infinity. It differs from the
Mandelbrot set
in that there is a different Julia set for each value of k. There is only one Mandelbrot set.
Alphabet Links
K
- Kinetic Energy
-
The faster things go the harder they hit you...
The energy an object has as a result of
its motion. Numerically the kinetic energy is equal to 1/2*m*v2
where m is the mass of the object and v is the magnitude of its
velocity .
Alphabet Links
-
Kinematics
-
An example of the relentless urge to name things...
The study of objects in motion without explicit consideration
for the forces which produced the
motion.
Alphabet Links
L
-
Lifetime
-
The time allotted to do the necessary...
Lifetime is the total
temporal
extent
of an object.
The amount of time run off in the lifetime of a clock
depends on some effects of relativity.
Alphabet Links
M
- Magnitude
-
Disregards possibly important information...
The size of a thing, without regard for its sign (+ or -) or
direction. Similar to the absolute
value of a number but applies to
vectors as well.
Alphabet Links
-
Mandelbrot Set
-
Benoit Mandelbrot had a set...
The Mandelbrot set, named for Benoit Mandelbrot, is the
set of all points c in the
complex plane
such that the
iterated
function
Zn=Z(n-1)2+c
does not
diverge
as n approaches infinity.
Alphabet Links
- Mass
-
Causes objects to hate to change speed...
The property of an
object which determines its resistance to changes in velocity. In the presence of a
gravitational field, as near the surface of a planet, the mass of
an object is proportional to its weight, the force exerted on the
object by the planet.
Alphabet Links
-
Mechanics
-
Having not much to do with automobile repair...
The study of objects in motion. Mechanics is normally limited
to a small number of large slow objects, as opposed to
statistical mechanics which deals with large numbers of objects,
relativistic mechanics which deals with objects moving near the
speed of light and quantum mechanics which deals with objects
more or less the size of atoms. Mechanics encompasses the topics
of kinematics and
dynamics.
Alphabet Links
-
Moment of Inertia
-
To rotation what mass is to linear motion.
-
The moment of inertia is the resistance an object offers to changes in
rotational speed. It depends on the mass of the object and the
distribution of that mass about the axis of rotation.
Alphabet Links
N
- Normal
-
Sticking straight out...
Another word for perpendicular, normal in this sense is
usually used in referring to a vector's
orientation relative to some surface. For example a vertical
vector is normal to a horizontal surface. I would not suggest that
on recovering from mental disease you tell people that you
feel perfectly perpendicular.
Alphabet Links
-
Now
-
The boundary between
future
and
past
where chance is converted to certainty...
Now – the current
instant. The duration of now is either zero or so
close to it that the difference does not concern us in the present context.
Alphabet Links
O
- Object
-
A thing, an element of stuff...
The term "object" is the most general form
of thingness. There are physical objects like baseballs and
uranium atoms, and mathematical objects like numbers and vectors . It will be clear from the context
what sort of object we are talking about.
Also the particle like aspect of fields, like the photon of
electromagnetic radiation or
gauge bosons
in general may be considered objects.
See the
notes on objects
for more.
Alphabet Links
- Origin
-
Where occupants of reference frames normally sit...
The point in a reference frame
from which measurements are made. It is the location of the zero
value for each axis in the frame.
Alphabet Links
P
- Parameter
-
Sort of controlling the shape of a function...
In an
equation
those elements that are not variables are parameters. If a parameter is
multiplied times a variable it may be called a coefficient. Parameters may be
fixed or adjustable. Fixed parameters are called constants. Adjustable
parameters are called control parameters. In the function
Y=A*exp(-(b-c*X)2)
A, b and c are parameters. If A takes on different values during different runs
through the values of X, it is considered a control parameter. If b is fixed
during all runs through the values of X, it is a constant.
The parameter c is a coefficient of X.
Alphabet Links
- Particle
-
Objects of trifling size...
An object whose size is negligible in
the context of our observation of it. For example the Earth might
be considered a particle if we were studying its orbit around the
Sun, but not if we want to know anything about its rotation about
its axis. The nucleus of an atom might be a particle in an
experiment on elastic
scattering , but not in considering nuclear fission.
Alphabet Links
-
Passive State Change
Requiring minimum effort on the part of Nature...
A passive state change is the change in state of an object
that results from the object's interaction only with the
spacetime it inhabits.
-
Entry text
Alphabet Links
- Period
-
Having nothing to do with punctuation...
The interval of time between the occurrence of identical states in a periodic system.
Alphabet Links
-
Past
-
Where some of the possible has become what happened...
The past is the
continuum
of
time
earlier than the
now.
Alphabet Links
-
Periodic
-
Exactly repetitive...
A dynamical system or
function which at
some point returns to the same
state or value. If a system or function ever revisits the identical state or
value it will continue to come back to it again and again in equal intervals of
time. That is why we call such a system periodic.
Alphabet Links
- Phase Angle
-
Slides a periodic function along the axis...
The offset from the origin of a
periodic
function
like the sine or cosine. For example in the function x=A*sin(w*t + f), f is the phase angle. The units on f are radians.
Alphabet Links
- Phase-Control Space
-
Spanned by parameter and variable...
If in a
phase space
representation of a
dynamical system
we exchange the roles of a
control parameter and the independent variable,
allowing the former to vary while holding the latter fixed, the resulting graph
is plotted in a mixed space called phase-control space. See the
Order online course
for more information.
Alphabet Links
- Phase Space
-
A space without measure...
Sometimes as an aid in understanding what is happening in a
dynamical system
it is useful to mentally create a new kind of space. This space has dimensions
of the state variables for our dynamical system.
In the case of the pendulum, for example, it would be one dimension measured in
position and one dimension measured in velocity. Time might be considered a
third dimension of this "phase space", just as it might be considered a fourth
dimension of ordinary space.
Alphabet Links
-
Photon
-
Chunks of radiation...
A photon is the
particle
-like aspect of light or other electromagnetic radiation, a bundle of energy
localizable in
space. Photons travel at the speed of light regardless
of the reference frame in which they are observed, as predicted by
relativity theory. It appears that the electrical
forces between charged particles may be due to an exchange of photons that never
are detected except by their action in producing the force. Such photons
are called virtual photons.
Alphabet Links
- pi
-
Of pie are square fame...
The ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter is
named by the Greek letter pi (π). The numerical value
of pi is approximately 3.1415926.
Alphabet Links
- Position
-
Not of the sort preferred to a job...
The location of an object relative to some point we have
chosen to be the reference point. Position is a vector quantity.
Alphabet Links
-
Potential Energy
-
Energy unrealized...
The potential energy of an object is the
energy that object has as a result of its position relative to other objects. The
numerical value of potential energy depends on the nature of the
interaction of the object with its surroundings and the choice of
a position to be the zero energy point.
Alphabet Links
-
Present
-
An illusory slowing of the sweep of time...
The present is the slice of the recent past that we perceive
as our current moment. Perception being a rather sluggish process, it is
hopelessly outpaced by the advance of
now.
Alphabet Links
-
Proper Time
-
Time displayed on an observer's wrist watch...
On account of the effects of relativity
time flows at varying rates for different observers. This requires that we be
careful in specifying whose time we are talking about. The time displayed on
the t-axis of a spacetime diagram is the
reference frame time. Each observer in that reference frame experiences her
"own time", "eigenzeit" in Einstein's native language. In English that is
usually called "proper time". An observer's proper time is that displayed on a
clock that accompanies observer throughout her relativistic adventures.
Of course the proper time will depend on the time set on the clock initially so
in preparing a spacetime diagram it is customary to re-zero all clocks at the
time origin of the diagram. From that time on, the duration of each observer's
proper time unit as seen from the reference frame will depend on that observer's
relativistic status.
Alphabet Links
- Property
-
Generally not sold or traded...
A characteristic that is inherently associated with the
object which is said to have that property. For example the mass
of an object is one of its properties. So also might be color, density and many other characteristics.
Properties are classified as extensive or intensive. Extensive
properties increase in proportion to the size of the object, as
mass does for example. Intensive properties are independent of
the size of the object. The density for examples remains the same
if I cut an object in half and throw half of it away. Things like
an object's position or velocity are not considered to be properties
of the object. They are not a characteristic of the object only
but are also dependent on the reference frame in which the object
is located.
Alphabet Links
Q
- Quadratic
-
Sort of square-like...
A
function
involving the second and lower power, and none
higher, of the independent variable. A quadratic function may
contain x2 explicitly or it may contain terms like x*(1-x),
where the second power of x is implied. In general a quadratic
may be written as y=a*x2+b*x+c . For an
illustration of a quadratic function, see the Quadratic Derivative display
in the Rate of Change lesson.
Alphabet Links
- Quantity
-
Addressing the "How much?" question...
A numerical value either scalar or vector , which describes some attribute of an
object like its
position or its velocity . We
sometimes speak of physical quantities to signify that we are
talking about an object's properties
or attributes as opposed to a purely mathematical quantity.
Alphabet Links
-
Quantum Mechanics
-
A small scale sort of science...
Early in the twentieth century it became evident that the
state
of very small
systems
did not change in a continuous way. Atoms jump from one allowed state to
another, skipping over the forbidden states in between. Newton's laws of
classical mechanics are not equipped to handle situations like this so a new
approach was required. Quantum Mechanics evolved to extend classical mechanics
to very small systems. See the
notes on quantum mechanics for more.
Alphabet Links
R
- Radian
-
A radius out, along and back...
An angular unit of measure. A radian is an angle subtended by
an arc whose length equals one radius. Since the circumference of
a circle is 2* π *radius and a
radian spans an arc of one radius, there are 2*π
radians in a complete circle. So 1 radian equals
360/(2*π) degrees.
This is illustrated below.
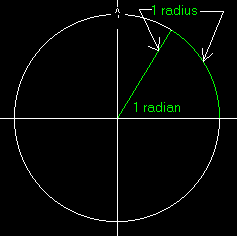
Alphabet Links
- Radius of Curvature
-
A fitting measure...
The radius of the largest circle containing the point at
which the radius of curvature is to be determined and fitting
within the curve. See the illustration below.
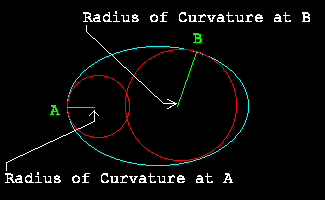
Alphabet Links
- Range
-
Where the dependent variable is at home...
The range is the
set
of values that the dependent variable of a
function may take on. A range may be finite as in the
set of numbers {1, 2, 3..n} or infinite as in all the numbers between 0 and 1.
Alphabet Links
- Reference Frame
-
A hypothetical construct of great usefulness...
A mathematical object which is used to allow comparison of
the positions in space of physical objects like particles, or the
comparison of one particle's positions at different times.
The reference frame may be made up of any set of coordinates which uniquely
specify a point in space.
See the reference frame notes for more.
Alphabet Links
-
Relativity
-
Einstein's way of keeping pyhsicists up at night...
The special theory of relativity deals with very fast moving objects. The
general theory deals with accelerated reference frames and gravity. A lot of
physics can be done without concern for these theories but where the effects
are felt, the results are profoundly different than what classical physics
would predict. I recommend that you at least see the
relativity notes if not read a good text on the subject.
Alphabet Links
S
- Scalar
-
Like plain vanilla numbers...
A scalar quantity is one having only
magnitude , not direction information. This is as opposed to
a vector quantity which has both magnitude
and direction.
Alphabet Links
-
Second Law
-
Time's arrow...
There is a law of nature that seems to be universal, applying to all sorts of
situations. It was initially formulated with respect to thermodynamics, the
study of heat flow. In that context the second law states that heat flows from
hot objects to cold objects with a consequent decrease in the hot object's
temperature and increase in the cold object's temperature. The temperature
changes reduce the distinction between the hot and cold objects, increasing the
entropy of the
system.
It is the tendency for entropy to increase over time that is the universal
aspect of the second law. This tendency is so ubiquitous that it has been taken
to define the direction of
time's
flow from
past
to
future.
See the second law notes for more.
Alphabet Links
- Set
-
One of the collective nouns of math...
In mathematics a set is a collection of related
objects. The mathematical usage is similar to the ordinary
English meaning of the word. The objects that make up a set are called the
elements of the set. If a set contains an unlimited number of elements it is an
infinite set. Otherwise it is a finite set.
Alphabet Links
- Shear Force
-
Not a filmy translucent thing at all...
Imagine a solid rectangular block of material with the bottom face held fixed on
the surface on which the block was resting and a force applied along the top
face... Sort of the same force you might apply to an Oreo cookie to slide the
top cookie off the bottom one to get at the cream filling. The applied force in
this situation is called a shear force. A solid block subject to this shear
force would be deformed so that its front face that was a rectangle becomes a
parallelogram.
Alphabet Links
- Significant Figures
-
No, no. Not that kind of figures...
The number of digits in a numerical value that are reliably
known. If the numbers being used in a calculation are measured
values, there will always be a limit on the accuracy of the
measurement. The results of any calculations based on those
numbers should not be reported with more significant figures than
the least accurate of the measured values. For example if the
length of a rectangle is measured to within 0.1 cm to be 25.3 cm
and its width to within 0.1 cm to be 6.6 cm, multiplying shows
the area to be 166.98 cm2. In significance arithmetic
the result however should be reported only to 2 significant figures
since the width is only known to that accuracy, giving an area of 170 cm2.
Alphabet Links
- Sine
-
O Lord, give us a sine...
In a right triangle, the ratio of the opposite side to the
hypotenuse. See the trigonometric functions
page for more.
Alphabet Links
-
Space
-
Invented by God to keep everything from being in the same place...
It is thought that at a very small scale space may be found to be quantized,
being made up of discrete steps. If this is true the length of the steps is
thought to be smaller than 10-34 meters. For our purposes we may
consider space a
non-temporal,
three-dimensional
continuum.
occupied by
objects
and
events –
that part of spacetime
where there is freedom of motion.
Alphabet Links
-
Spacetime
-
Space and time as a single entity...
An extension of the concept of space to include an additional dimension
perpendicular to the normal axes spanning our familiar three-dimensional
space. This additional dimension measures time so that a point in spacetime
locates an event. Since full four-dimensional spacetime is difficult to
picture, we frequently work in spacetime consisting of one or two spatial
dimensions and the time dimension. Spacetime is integral to Einstein's
relativity theories.
See the notes on spacetime
Alphabet Links
-
Spacetime Diagram
-
A convenient tool for exploring the effects of
special relativity is the spacetime diagram.
It is a plot of one dimension of space along the horizontal and the
time dimension along the vertical. The worldlines
of objects and individual events may be displayed on such a plot.
See the spacetime diagram notes for more.
Alphabet Links
- State
-
What state of affairs is this...
Dynamical systems evolve over
the course of time. The state of the system at any instant may be
identified by the values of certain variables at that instant.
For example specifying the angle from the vertical and the
velocity of a frictionless pendulum allows us to predict its
position and velocity at any future time. Therefore the state of
the pendulum at any instant is its position and velocity. In this
example the position and velocity are known as state
variables. See the state of a system
article for more.
Alphabet Links
-
State Variable
-
The keys to the future...
An observable quantity which must
be specified in order to determine how a Dynamical systems changes over the
course of time. In conservative
systems if all the state variables are known at any instant,
the state of the system is determined
for all future time.
Alphabet Links
-
System
-
A collection of objects and interactions...
For our purposes a system is a set of
objects
interacting in accordance with certain laws of nature. There is a degree of
arbitrariness in defining a system. We get to choose what to consider to be the
system and everything left over is the system's environment. If our system
behaves in unexpected ways the first place to look for problems is in the system
definition. Perhaps we have not included all the pertinent pieces in our system
definition.
See the system notes for more.
Alphabet Links
- Systéme International
(International System) (SI) Units
-
Lightening the load on conversion factors...
The most commonly accepted system of units in scientific
work. The fundamental units in this system are the meter,
kilogram and second. See the
Wikipedia article for more.
Alphabet Links
T
- Tangent
-
That which one sometimes goes off on...
A straight line which touches a curve in one and only one
point. The slope of a tangent is the slope of the curve at that
point. Slope is the change in the vertical coordinate divided by
the corresponding change in the horizontal coordinate. See the Rate of Change lesson for more on
slopes.
- Also, in a right triangle, the ratio of the opposite side to
the adjacent. See the trigonometric functions
page for more.
-
Tangential Velocity
-
The slingshot trick...
Tangential velocity is a term often applied to rotating wheels or orbiting
satellites. It is the component of
velocity tangent to
the rim of the wheel or the satellite orbit.
Alphabet Links
-
Temporal
-
The timewise aspect of a thing...
Temporal – of or relating to
time.
Alphabet Links
-
Time
-
Invented by God to keep everything from happening at once...
It is thought that at a very small scale time may be found to be quantized,
being made up of discrete steps. If this is true the duration of the steps is
thought to be smaller than 10-34 seconds. For our purposes we may
consider time a non-spatial
continuum
in which
events
along a
worldline
occur in irreversible succession.
Alphabet Links
-
Trajectory
-
A path best avoided...
The path an object takes through space. Frequently associated
with a projectile like a bullet or a missile.
Alphabet Links
U
-
Universality
-
There is one of these critters under every rock...
Universality refers to the fact that a certain number, approximately 4.669,
discovered by Mitchell Feigenbaum and called Fiegenbaum's number, keeps popping
up in what appear to be totally unrelated circumstances. See the
Order online course
for more information.
Alphabet Links
V
- Vector
-
Are these the arrows of outrageous fortune?...
A quantity having both magnitude and
direction. The direction may be expressed as an angle from a
single axis in two dimensions. In three dimensions, the direction
must be a pair of angles measured from different axes. On free body
diagrams vectors are represented by arrows. See the
vector arithmetic page for
ways in which vectors may be combined.
Alphabet Links
- Velocity
-
Lying between acceleration and displacement...
The speed of an object in a given direction. Velocity is a vector quantity.
Alphabet Links
W
- Wavelength
-
An important consideration in interference...
The distance covered by a travelling wave in one period . It is the distance between points of
the same phase angle in a travelling
wave. For example the distance between peaks, or the distance
between valleys of a wave train. The wavelength is frequently
symbolized by the Greek letter lambda
l .
Alphabet Links
- Work
-
All work and no play makes Jack...
Work is defined as the application of
force over some displacement .
Numerically the work done is the product of the force and the
distance moved in the direction of that force. This may be
calculated as force times displacement times the cosine of the angle between force and
displacement. The angle gets involved because things do not
always move in the direction in which you push them.
Alphabet Links
- Worldline
-
A track on the sands of time...
A worldline is path through spacetime
connecting the events in which a particular
object
participates including the sort of null event "object found here". The worldline
is a record of the object's history. The time scale along an object's worldline
will vary depending on the relativistic history of the object.
Alphabet Links
X
-
-
No entry here yet
Alphabet Links
Y
-
-
No entry here yet
Alphabet Links
Z
-
-
No entry here yet
Alphabet Links
|
|
|
|




